Intel microprocessors in 80s
Intel is the world's leading producer of processors. In the second part of the 70s, Intel has begun to produce processors with VLSI technology.
Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI) had made possible to put first tens of thousands, then hundreds of thousands, and finally millions of
transistors on a single chip; it means smaller, faster and economic computers. The personal computer (PC) era had begun and Intel
was at the forefront producing powerful CPU in the 80s and believing in the PC.
Intel 8088
The processor 8088 was created by Intel in 1978. It is based on the revolutionary Intel 8086, the first processor with a x86 architecture.
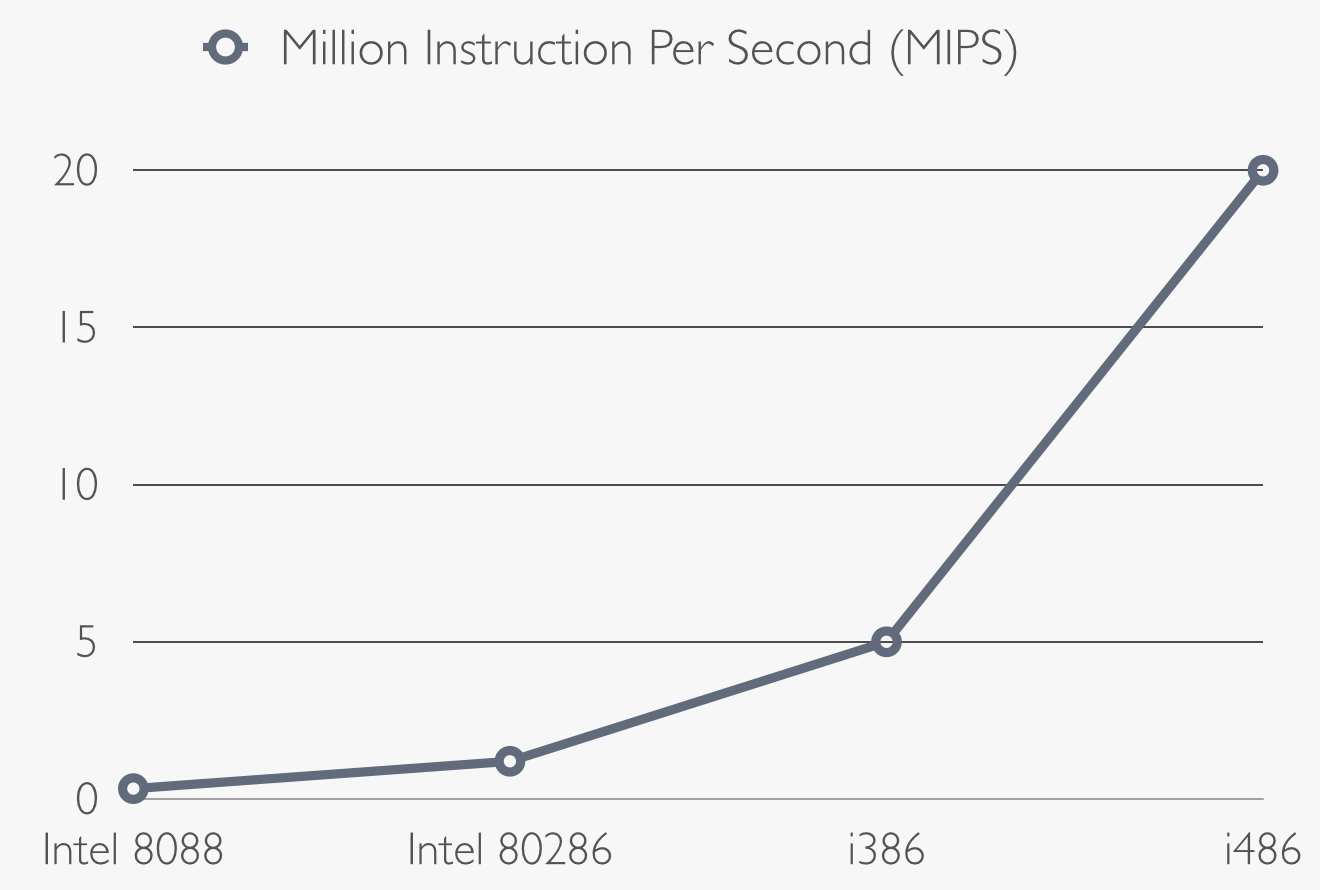
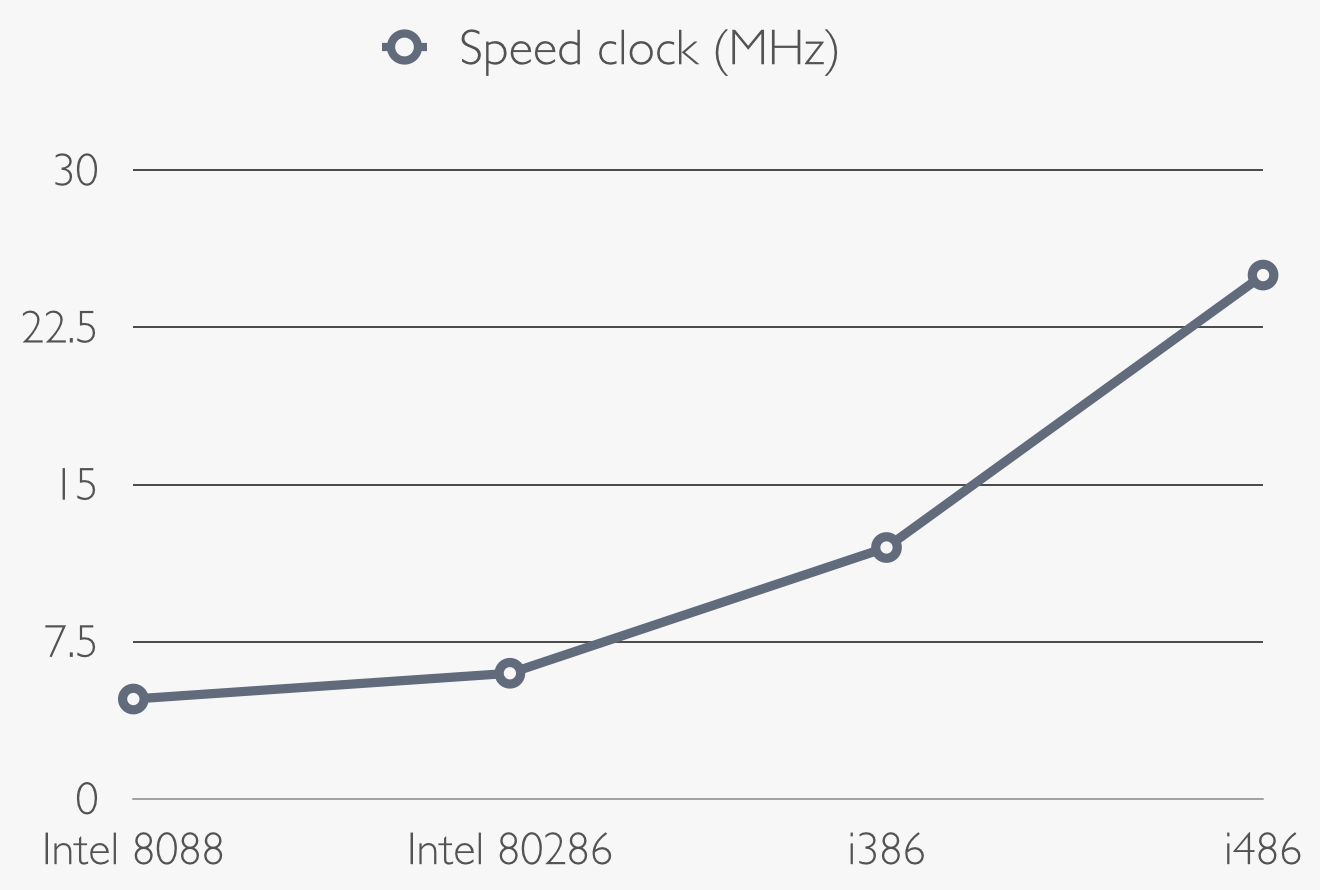
Intel 8088 is cheaper and slower then the 8086: it's 16-bit microprocessor and it works with a frequency of 4,77 MHz whit 0.33 MIPS (million of instruction per second),
but it has a external data bus width of 8 bits (not 16) and it is compatibility with 8-bit support chips.
The Intel 8088 is the processor of the first IBM personal computer (IBM PCjr), it has been projected to work in a office or home machines.
The key of the succes of this microprocessor was joined the hight speed performance of the 16-bit Intel 8086 whit the new x86 architetture
and the support for the economic 8 bit chips. In this way Intel and IBM had created a larger market for computers, the IBM personal computers.
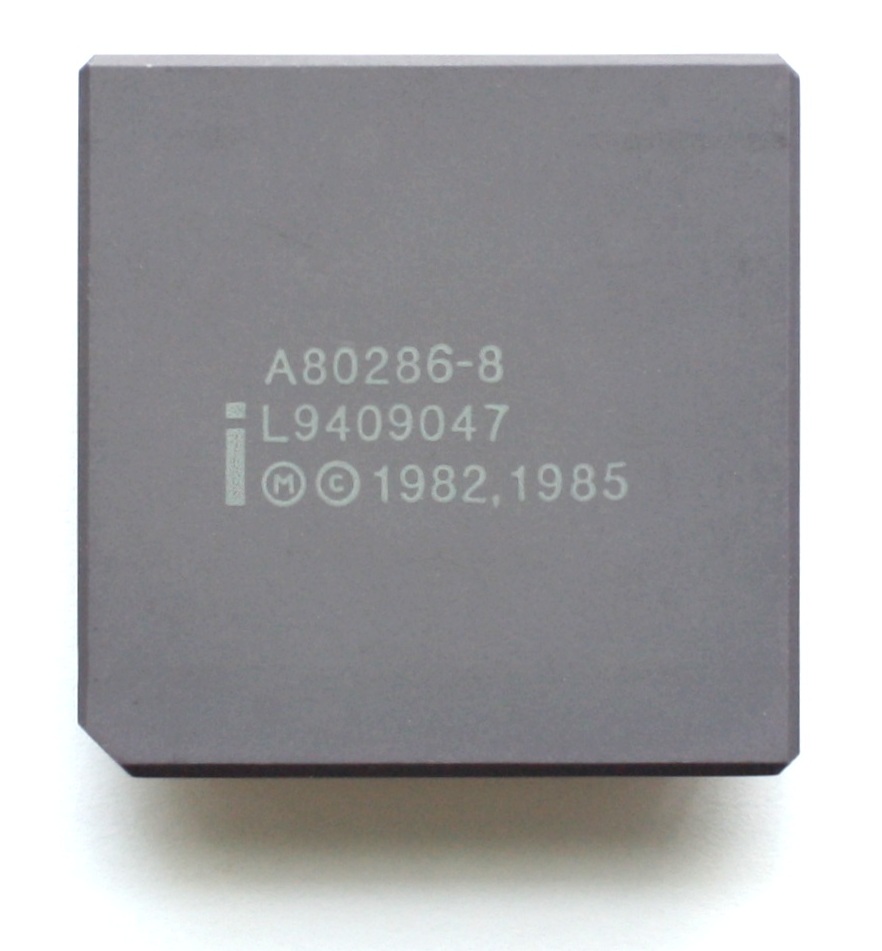
Intel 80286
The Intel 80286 was introduced in 1982 and it was used in the IMB pc until 1990 and the performance was more then twice that of its
predecessor (Intel 8088). Indeed it is a 16-bit microprocessor with a clock speed of 6 MHz, 1.2 MIPS and it was able to use 16 MB of RAM.
In the frist years this microprocessor was too expensive and there wasn't softwere developed to
the hight performance of the Intel 80286; but it was the
first processor compatible with the previously software and it was designed for running
multitasking programs as real-time process control or multi-user system.
The Intel 80286 is a microprocessor built for the second generation of PC, the generation
of the graphical user interface, that's why this processor had been running for all the 80s.
Intel 80386 and Intel 80486
The Intel 80386 or i386 was introduced in 1985 and it is the frist Intel 32-bit microprocessor.
This processor has not change the sales of the Intel 80286 because it needed to a new expensive motherboard to work,
but it is faster and faster then its predecessor.
The first i386 has a frequency of 12 MHz, it can compute 5 MIPS and it has the new 32 bit register inside the CPU,
which permits to count huge numbers.
In the 80s there was a war between RISC and CISC architetture. In 89, the common thought was that
RISC was the winner because this kind of CPUs are faster and economic.
The successor of the i386 it's the Intel 80486 or i486, released in 1989. It is the frist CISC and
RISC architetture CPU, the first pipelined x86 microprocessor and the fist chip to use more then a million of transistor.
Intel did't change the structure of its microprocessor converting it into RISC because there was the issue
of backward compatibility and the billions of dollars companies have invested in software for the Intel line.
In addition to Intel has been able to implementing the RISC architetture in a CISC microprocessor.
The Intel CPUs contain a RISC core that executes the simplest (and typically most common) instructions speedily, while the complex instructions are
interpreted in a CISC way.
The i486 instructions is faster even because it uses the pipeline architetture:
A pipelined CPU is a technique to increase the speed of the CPU. Indeed the processor is divided into
sectors which can execute operations independently, in this way an instruction
doesn't need to wait for the conclusion of the command before it, but when the fist sectors is
free a new instruction can become.
All this means hight performans, indeed the i486 offers two-and-a-half times the performance of the i386 at the same
clock speed and the version with 25 MHz computes 20 MIPS.
The i486 has been replaced by the fourth generation of microprocessor, the Intel pentium, in 1993; it is a 64-bit microprocessor wich opened the market of the desktop pc, while
the less expensive (in energy and in prize) i386 and i486 were the best solution for the new market of the notebooks.
External Links
- [Visited on 06/11/2014] Intel 80286(picture), Wikipedia copyright, Creative Commons license.
- [Visited on 06/11/2014] Intel 80386 and Intel 80486(picture), Publicity photograph.
- [Visited on 03/11/2014] Intel 8088 - Wikipedia
- [Visited on 03/11/2014] Intel 80286 - Wikipedia
- [Visited on 03/11/2014] Intel 80486 - Wikipedia