The evolution of the portable storage devises in the 70s-80s
A portable storage devise is a secondary memory which can be written and read by a computer and
it can be easily removed from the computer to storage the content in an other computer.
The job of the portable memory devices is to storage and to share data, the only differences between the
different devices are the limit of storage and the speed of writing and reading data.
The fist portable storage devise, with many limitations, is the Punched Card (1890), but the floppy disk is the first commercial
device convenient to storage data and personal data.
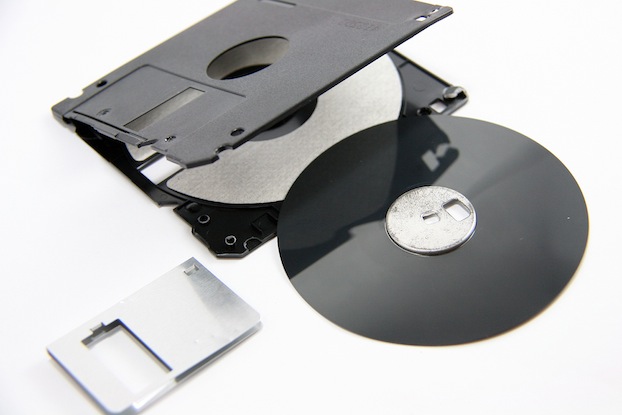
A floppy disk is a little disk magnetizable (as music tapes). It can store informations (bits) because it's made by a
material treated with iron oxide: it's a ferromagnetic material and when it is exposed to a magnetic
field for a certain period of time it remains magnetised.
From the 8-inch to the 3.5-inch disk
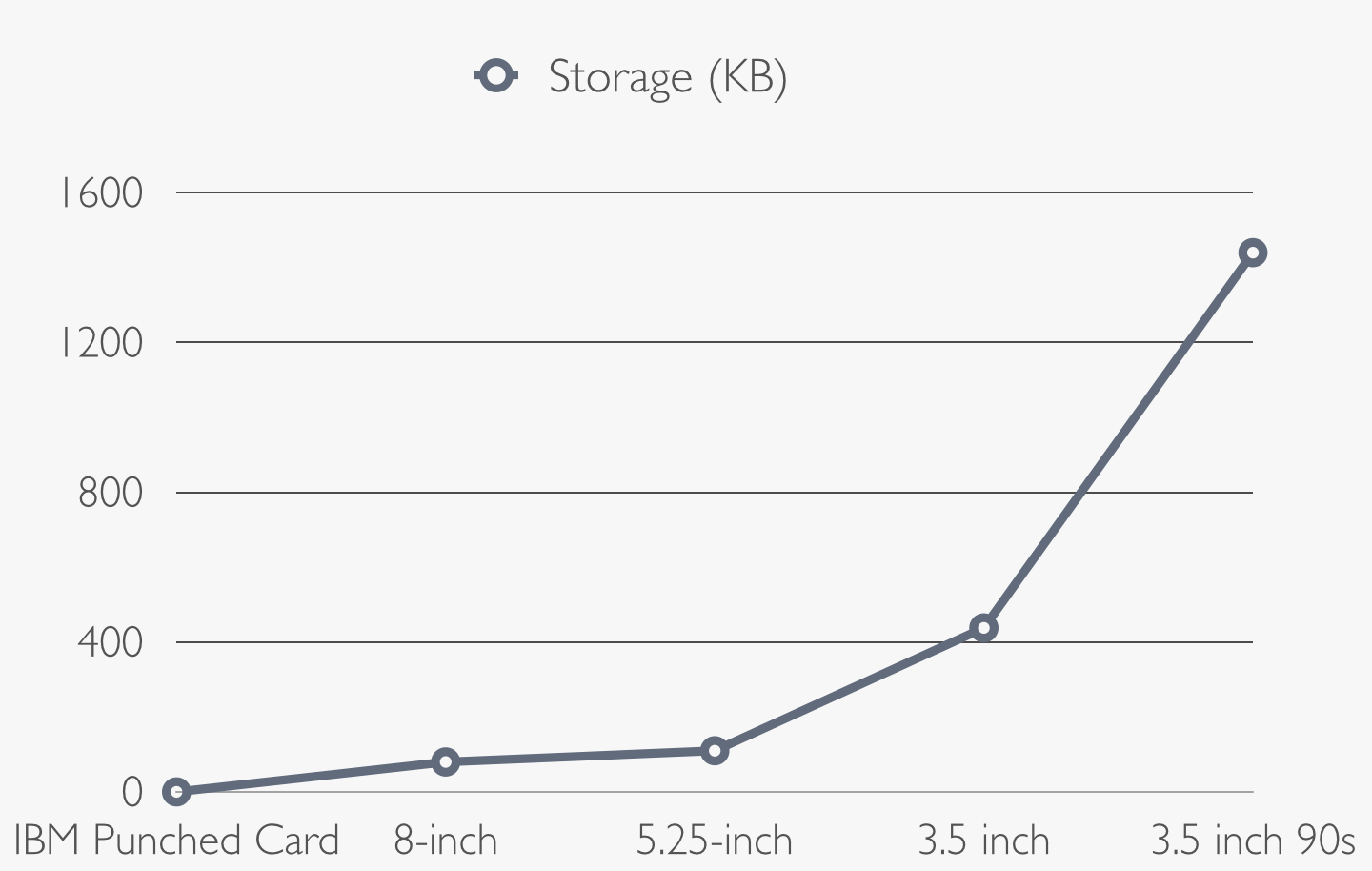
The floppy disk drive (FDD) was invented at IBM by Alan Shugart in 1967. The fist floppy disk were a 8-inch disk (size of 20 cm)
with the capacity of 80KB of storage. It was called "floppy" because the first version of it was flexible.
The floppy disk was developed by IBM for storage the informations of manutention of their mainfreme, but
soon the producers of personal computer become to distribuite their softwere and their DOS using the floppy disk.
The Floppy was commercialised only in 1971 and the fist personal computer with the compatibly for the floppy disk was the Olivetti
P6060 in 1975.
A floppy disk has the same characteristic of an hard disk (press the link for more informations), except that in a floppy disk the
head of the floppy touches directly the disk and for this reason a floppy disk get ruined; it has a life of 20 years, also because
when the computer are not writing or reading it, the floppy stops it's rotation to preserve itself.
Alan Shugart left IBM to found his company in 1973. He produced a economic 8-inch disk whit a storage of 800 KB in 1975,
it offered for the first time a low-cost drive for the emerging personal computer market.
However a 8-inch drive was too big for the personal computer, that's why the Shugart lab produced a 5.25 inch disk
in 1976 whit a capacity of 110 KB.
In the early 80s a 5.25 inch floppy disks duble-sided had a capacity of 360 kB and the smaller dimensions and the chipper prize
contribute for the succes of this device in the market. Indeed they were used mainly by private users, for example
the apple II (one of the solder personal computer of those era) has a 5.25 inch floppy drive.
The Japanese company Sony developed a 3.5 inch floppy disk in 1980. This kind of floppys have a storage of 438KB
(up to 1.44MB in the following years). in addition to they are smaller and they have hard-shell cartridge and an automatic shutter,
that closed over the recording surface, when it was removed from the drive.
The leader company IBM pushed for the 5.25 inch but gradually this bigger floppy were replaced by the more comfortable 3.5 inch floppy disk,
which had already the capacity of 700 KB or even 1.44 MB.
From the Cassette Tape to the Compact Disk
Cassette Tape
A Cassette Tape was a magnetic audio tape that in the 70s could hold 660kB of storage per side.
It was the easiest, cheapest way to store data until the floppy disk became more accessible and less expensive.
The biggest difference between the Tape and the floppy is that the Cassette Tape has a sequential access ( you need to slide the tape to
arrive to the data or the song you wish), while the floppy disk has a direct and speed access to the data. With the floppy circular structure it's
possible to read all the sectors of the disk. Indeed, from the 80s, the Cassette Tapes were mainly used just as music cassette.
Compact Disk
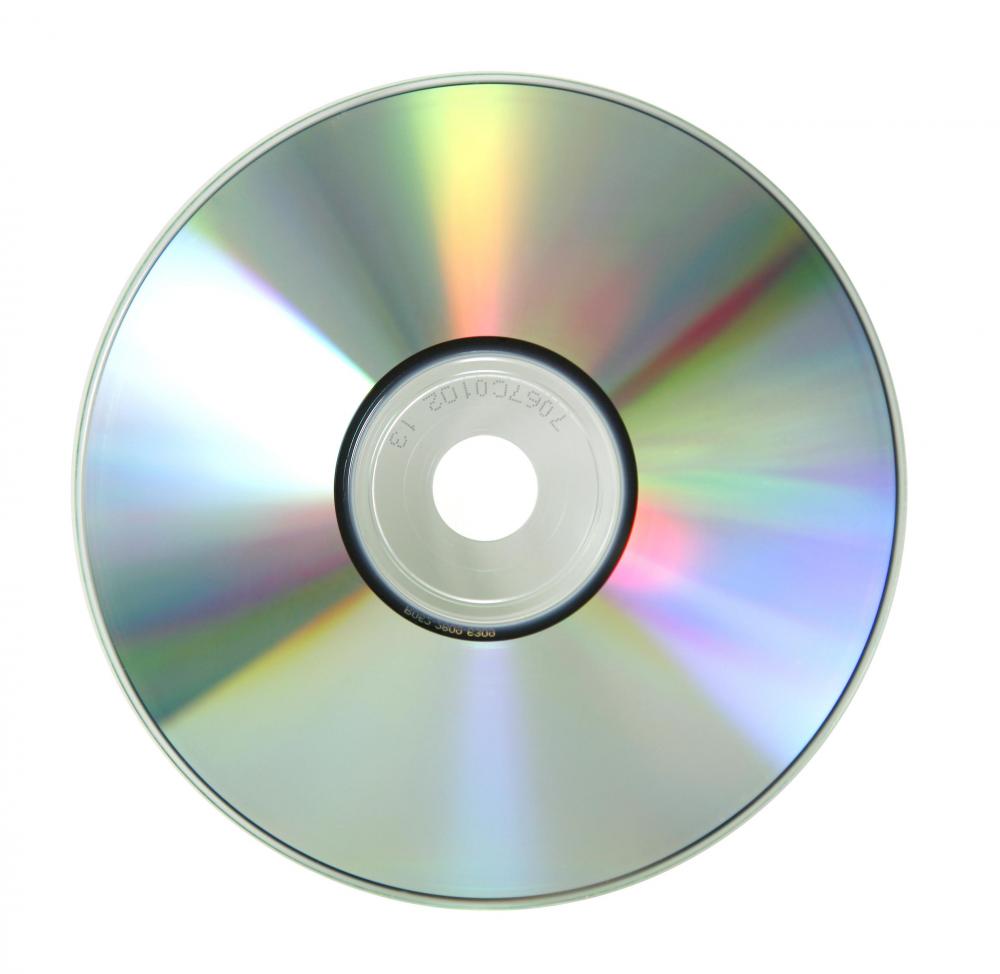
The company Philips and Sony first published the compact disk (CD) in 1979. The CD works
with a disc of polycarbonate with inside a thin sheet of polycarbonate where a hight energy laser creates depressions. The depressions in the polycarbonate sub- strate are called pits;
the unburned areas between the pits are called lands. A low energy laser can read the the pits and lands as signals of 0 or 1. The datas are
written in a single continuous spiral starting near the hole and working out a distance of 32 mm toward the edge.
The users can not overwrite a CD. Indeed the CDs (as the music tape) were used to store music data; But the vantage of the CD is not just the possibility to skip quickly
between the songs. Philips published the yellow book in 1984, the manual to define the standard constration of a data CD. A data CD looks
like to a music cd except for the implementation of a detection and correction code. Then, always Philips defined a method to store audio, video and data
in a same sector of a CD.
In this way a CD become useful for distribuite music, video, softwere, and generic datas, a technology more useful then the Cassette Tape.
FFD or CD
Even if a CD can storage more datas then a floppy disk, it can not be rewritten, indeed the PCs had been having the floppy drive until the 95, the age of
the compact discs recordables.
A CD-R (Compact Disc-Recordable) is a variation of the compact disc available in 1988. It can be written one time, but in 1990 a CD burner
still cost thausend of dollars. It was a expensive way to storage data until 1995, when a burned CD become economic and it assumed the dimension of a CD.
Only the CD-RW (Compact Disc-Rewritable) in 1997 became confortable as a floppy disk for storing and sharing personal data; even if in 2000 was born the fist USB,
the CD was read faster from the computer and it become a common way to storage data as backup whit it's 760 MB of storage.

External Links
- [Visited on 06/11/2014] A disassembled floppy disk, creative Commons license.
- [Visited on 05/11/2014] Floppy disk - Wikipedia
- [Visited on 05/11/2014] Floppy disk - howstuffworks
