Ethernet
History
Ethernet is a computer networking technology used in Local Area Networks and created in 1973 by Robert Metcalfe while He was a researcher at the Xerox Corporation's Palo Alto Research Center(Xerox PARC). The idea for Ethernet was largely inspirated by ALOHAnet, another storically important computer network, that Metcalfe had studied as part of his PhD dissertation. He developed both the physical method for connecting the devices and the standards for monitoring the communication.
In 1979 Metcalfe co-founded the 3Com Corporation with the intention of commercialize Ethernet. 3Com started by building Ethernet circuit board for minicomputer but later they built an Ethernet card mostly known as NIC (Network Interface Card).
He also succeed convincing Intel, Xerox and DEC working together and promote Ethernet as a standard for LAN networks.
On September 30, 1980 the three companies published "The Ethernet, A Local Area Network. Data Link Layer and Physical Layer Specifications" creating the earliest Ethernet standard. Version 2 was released on November 1992.
Ethernet battled against IBM's token ring and General Motor's token bus , two differents LAN standards. At the end of 80s 3Com shifted from coax cables to twisted pair cables and finally won the battle becaming the dominant local area network technology.
3Com has been bought by Hewlett-Packard on April 12, 2010. Since the aquisition 3Com has been fully absorb and no longer exists as a separate society.
Technology
Bus topology
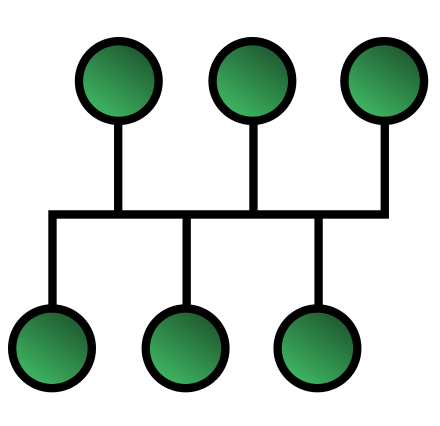
The architecture of the original Ethernet used a bus topology where each computer is connected to a single cable. This implementation turn out in a broadcasting comunication, where all the messages are received by all the computers connected to the network.
There are several advantages using this kind of architecture. The network is very cheap and it's possible to connect a new device easily without modifying the entire system, a great plus for a network administrator. On the other hand there are also some problems, two computers could start sending informations through the cable at the same time resulting in a collision that inevitably compromises the messages.
The collision issue is solved by a scheme known as Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Detection (CSMA/CD) which govern the way the computers shared the channel. First of all each station ensure that the line is free before starting to send data. If a collision anyway occure both the stations detect it and stop transmitting data, then they wait a random amount of time and after that try to transmit data again. The collisions issue could start being a problem for high traffic networks.
The files are not delivered completeley in one step but split in several sections called frames. Each frame follow a specific format shown in the figure below. The file contains both the origin and destination address. Since each station receive all the frames delivered in the network it will just check the destination address of them, keep the right frames and get rid of the others. This behaviour could be an issue since a station set in a promiscuous way could just sniff all the frames, even that frames which are not suppose to be delivered to it.

Star topology
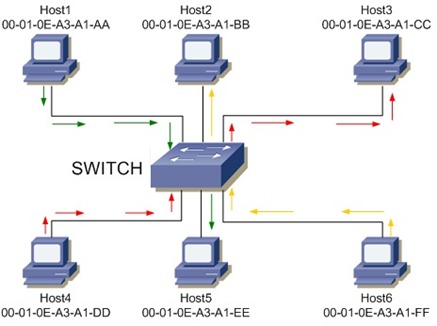
The introducing of hubs and switches was a giant leap for Ethernet networks. A switch is a computer network device that connect stations together using a form of packet switching to deliver datas at the right destination. This mean that every station in connected to the switch only. As soon as the switch receive a frame it analyze the destination address and pass the frame on to the channel connected to the right device. An hub is just a simpler version of the switch where every frame is redirect to all the lines instead of only the right one. The combination of switches and full-duplex connections eliminate the problem of collisions since each Ethernet section is now isolated.
Evolution of Ethernet
During the years the physical layer components such as cable, connectors ecc evolved improving the speed and reliability of Ethernet.
An Ethernet controller runs at the speed of the slowest connected device, which is helpful when mixing old and new technology on the same network.
| Name | Standard Clause | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Experimental Ethernet | No Standard | The original Ethernet implementation was 2.94 Mbit/s fast and used a coaxial cable. |
| Thick Ethernet | 10BASE5 | The first standard Ethernet, it used an AMP 228752-1 connector also known as "vampire tap" that literally tap a connection by drilling into the cable. It had a 10 MBit/s speed and used a bus topology with collision detection. |
| Fast Ethernet | 100BASE-T | A term that include all the three standards for 100 Mbit/s over twisted pair cable. All of these use a star topology. |
| Gigabit Ethernet | 1000BASE-T | Released in June 1999, all the variants and successive Ethernet versions use a star topology. The 1000BASE-X version use fiber optic cable while the other versions still use twisted pair cable. |
| 10Gbits Ethernet | 10GBASE-SR | Released in 2002 it's ten times faster the the predecessor, most of the versions use fiber optic cable. |
| 40Gbits Ethernet | 40GBASE-KR4 | Released in June 2010, on 2014 it's the latest version of Ethernet. |
External Links
- [Visited on 06/11/14]Wikicommon image
- [Visited on 06/11/14]Wikicommon image
- [Visited on 06/11/14]Prof. Marcelo Moreira's slides
- [Visited on 06/11/14]JDSU Fundamentals of Ethernet
- [Visited on 06/11/14]Encyclopaedia Britannica
- [Visited on 06/11/14]The evolution of the Ethernet Local Computer Network
- [Visited on 06/11/14]A guide for building a thick-Ethernet network... updated 2012.
- [Visited on 06/11/14]Robert Metcalfe's video about the history of Ethernet
- [Visited on 06/11/14]Robert Metcalfe's talking about the first Ethernet LAN
- [Visited on 06/11/14] Image taken from Wikimedia Commons. Fair use intended.