Intel 8085 and Intel 8086

Intel 8085
The Intel 8085 is an 8-bit microprocessor introduced by Intel in 19765. With improvements in integration technology, Intel integrated additional chips required by the 8080, i.e. the 8224 clock generator and 8228 sustem controller, within a single chip to form the Intel 8085. It was the first Intel's microprocessor with NMOS Technology. The NMOS Technology offered faster speed and higher density than PMOS. The processor was designed using NMOS circuitry and the later "H" versions were implemented in Intel's enhanced NMOS process called HMOS, originally developed for fast static RAM products. Intel made the 8085 as a significant improvement on the 8080, both in performance and handling issues. It has improved hardware by only using +5V power (the 8080 required +5V, -5V and +12V).
Intel 8086
The Intel 8086 is a 16-bit processor designed in 19786. Stephen Morse was the sole designer for the Intel 8086. It gave rise to the x86 architecture which helped transform Intel from merely one of many chip companies to the world's largest producer of microprocessors. Its advanced multitasking capabilities and memory-management circuitry would be built right into the CPU, allowing operating systems to run with much less program code. The Intel 8086 microprocessor was manufactured first using depletion-load NMOS circuitry and was soon moved to a new refined NMOS manufacturing process called HMOS(for High performance MOS). This was followed by HMOS-II, HMOS-III versions, and, eventually, a fully static CMOS version for battery-powered devices, manufactured using Intel's CHMOS processes. The 8086 has complete 16-bit architecture, 16-bit internal registers, 16-bit data bus, and 20-bit address bus (1 MB of physical memory). This was a big advancement over 8085 and thus it laid platform for the famous x86 architecture.

Tech Specs
| Specifications \ Name 1 2 3 4 | Intel 8008 | Intel 8080 | Intel 8085 | Intel 8086 |
| Technology | PMOS | NMOS | NMOS/HMOS | NMOS/HMOS/CHMOS |
| CPU clock rate | 0.5 MHz | 2 MHz | 3 MHz | 8 MHz |
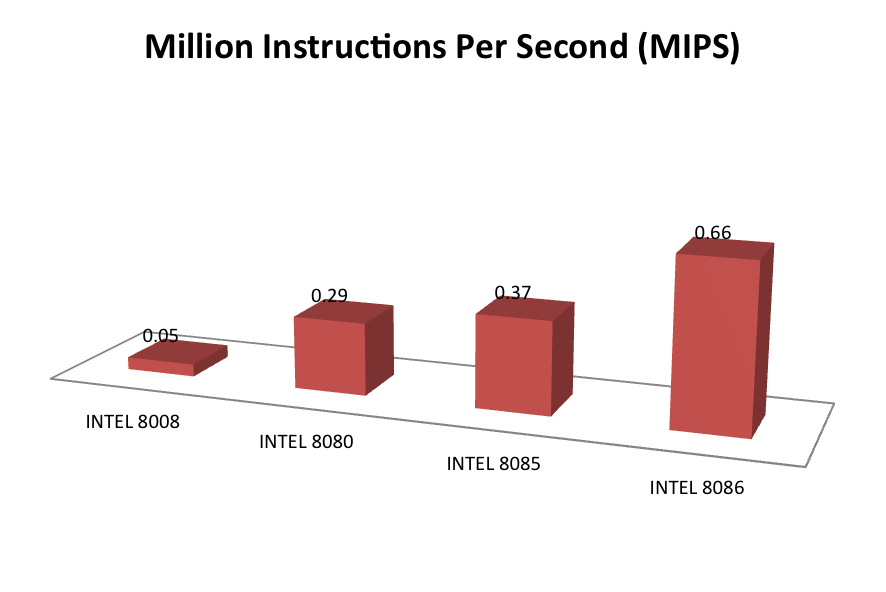
| MIPS | 0.05 | 0.29 | 0.37 | 0.66 |
| Addressable Memory | 16 KB | 64 KB | 64 KB | 1 MB |
| Min. feature size | 10 μm | 6 μm | 3 μm | 3 μm |
| Transistors | 3,500 | 4,500 | 6,500 | 29,000 |
| Packages | 18 pins DIP | 40 pins DIP | 40 pins DIP | 40 pins DIP |

External Links
- [Visited on 05/11/2014] CPU world 8008
- [Visited on 05/11/2014] CPU world 8080
- [Visited on 05/11/2014] CPU world 8085
- [Visited on 05/11/2014] CPU world 8086
- [Visited on 05/11/2014] Wikipedia 8085
- [Visited on 05/11/2014] Wikipedia 8086